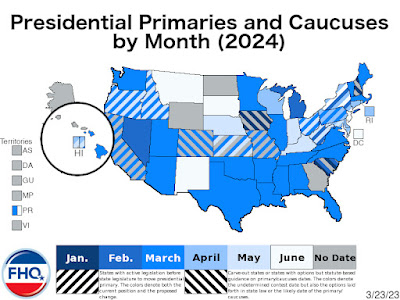
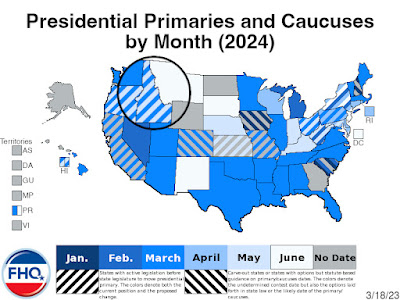
It has been a pretty bad stretch this last little bit.
Mentions of the
2024 presidential primary calendar have increasingly peppered articles, op-eds and other news items in recent weeks. And why would they not? 2024 is approaching. The process is heading into the thick of candidate announcement season. Things are heating up as the invisible primary progresses and becomes more visible.
But there is a problem. These calendar blurbs keep getting it wrong.
It started with
Karl Rove writing in the Wall Street Journal a few weeks back. He correctly noted that Iowa caucuses and New Hampshire primary have no dates yet, but then he moved on to South Carolina. "
Democrats are trying to shift the primary there from Feb. 24 to Feb. 3." The South Carolina primary is
not scheduled for February 24. It was
never scheduled for February 24. February 24
does happen to be on the last Saturday in February, the day on which South Carolina Democrats held their 2020 presidential primary. But the state parties in the Palmetto state set the dates of the primaries. It is not set in state law. In other words, there is no state law with a specific date that carries over from the previous cycle. It resets to nothing -- there is no date -- every cycle.
Then it was
Richard Winger at Ballot Access News who picked up on the South Carolina theme. But in his case, it was talk of the Republican process in the typically first-in-the-South primary state. And again, the date quoted for the South Carolina contest in a post that has subsequently been edited was February 24. As with the South Carolina Democratic presidential primary, the contest on the Republican side has and has had no date. The Republican Party will make that decision later this year sometime, likely at a point when the decision makers within the party can insure that the primary will be first-in-the-South and/or third in the calendar order as called for in Republican National Committee (RNC) rules.
Not a one of those descriptions is correct. None of them. There are
no dates for any of those contests. Not Iowa. Not New Hampshire. Not South Carolina (Republicans). And just a cursory dig into any of those supposed dates -- February 5, February 13 and February 24 -- leads to one place:
The Green Papers.
Look, I love The Green Papers. The value of that storehouse of information built by Richard and Tony is immeasurable. I still cannot believe my dumb luck in stumbling on the page in 1999 working on an undergraduate paper in George Rabinowitz's US national elections class. I frequently cite The Green Papers here at FHQ. Heck, their site is perpetually linked in the right sidebar. I would not do that unless I trusted the information they provide.
However, I take issue with how The Green Papers deals with the dynamism of the evolving presidential primary calendar every cycle. It is a philosophical difference. The Green Papers is willing to carry over dates from the previous cycle, whether there are actual dates for contests set by state law or not. And FHQ is very simply unwilling to suspend our disbelief and "presume" that the Iowa caucuses, for example, will fall on Monday, February 5, 2024.
Well, actually, FHQ is unwilling to do that now. But in January 2021, when FHQ posted its first iteration of the 2024 presidential primary calendar, it made sense to slot Iowa into a February 5 slot. And if Iowa could be tentatively penciled in there on the calendar, then the remaining three early states could easily be shifted into similarly tentative spots all before Super Tuesday on March 5. That is what the initial FHQ calendar showed.
But the information environment around those tentative early state dates did not hold for long. And it did not hold because six months into 2021, Democrats in unified control of state government in Nevada established a state-run presidential primary in the Silver state. Not only did decision makers in Nevada shift from caucuses to a primary, but in the process they staked a claim on a first Tuesday in February calendar position that broke with the previous conception of the early calendar order. Theirs was a move to make a case to be first in the order, or to set the stage to make a case to be first in the order.
Yet, at that early stage of the invisible primary in mid-2021, not even the national parties had set their rules for the 2024 cycle. Although, at that point, a Nevada presidential primary set for Tuesday, February 6 meant that Iowa and New Hampshire (and South Carolina on the Republican side) would have to conduct contests before the first Tuesday in February to protect their traditional positions. That was known in June 2021 when that Nevada presidential primary bill was signed into law.
In other words, it was clear then that a February 6 Nevada presidential primary meant that Iowa, New Hampshire and possibly South Carolina Republicans would not fall on February 5, February 13 and February 24, respectively. That view was further buttressed a year ago this month when the RNC adopted its rules for the 2024 cycle, rules that once again protected the early positions of Iowa, New Hampshire, Nevada and South Carolina. Granted, there was still uncertainty at that point in April 2022. The Democratic National Committee (DNC) had not yet set its calendar rules for 2024, but
serious talk of an early calendar shuffle had already begun, talk in which
Nevada's position prominently figured. And even if national Democrats signed off on an earlier Nevada primary, Silver state Republicans could still opt out and hold caucuses at a later date.
But at that point, in the late spring of 2022, a Nevada Democratic primary on February 6 still would have meant that February 13 -- a week later -- would be off the table as an option for New Hampshire, given the state law in the Granite state and how decision makers in the office of the secretary of state have behaved, despite national party rules, in the past. And as New Hampshire goes, so too does Iowa often go. February 5, then, likely would not have been an option for Iowa Republicans.
Of course, any real discussion of February 5 Iowa caucuses or a February 13 New Hampshire primary died, or started to officially die, on December 1, 2022 when
President Biden sent a letter to the DNC Rules and Bylaws Committee (DNCRBC) on the eve of its meeting to decide on the states that would get waivers to hold early presidential nominating contests in 2024. The information environment around the 2024 presidential primary calendar again shifted. The votes at the
December 2, 2022 DNCRBC meeting and the
February 4, 2023 DNC meeting solidified the decision to schedule the South Carolina Democratic primary on February 3. Most uncertainty that had existed about the Democratic calendar was extinguished that day. The question then was not whether Iowa and New Hampshire would settle for February 5 and February 13 slots respectively. Instead, the question was how far ahead of the South Carolina Democratic primary the two traditionally first states would jump.
At this point in the 2024 cycle, the Iowa caucuses are not set for February 5. They are not "presumably," to adopt the tag used by The Green Papers, set for February 5. The same is true for the New Hampshire primary and February 13. Those dates are wrong. They serve no purpose other than to obliquely suggest that those were the dates of the Iowa and New Hampshire contests in the last cycle. And when folks miss that oblique reference and run with the wrong dates, they are misinforming their readers.
It is and has always been FHQ's mission to better inform people about this complicated process. We can do better than presuming dates from the last cycle carry over to the current one. They do in a great many cases, in instances where there is a state law or state party rule that clearly defines a date for any given delegate selection event. And there are laws in both Iowa and New Hampshire that dictate, and have dictated, where the contests in those states will end up. Those laws are specific as to the position, if not the date, of those contests, seven days prior to another primary in New Hampshire (as has been the interpretation) and eight days before another contest in Iowa. If actors in the Hawkeye and Granite states do what they usually do (or what they have signaled in 2023 that they will do in 2024), then both contests will fall some time in January 2024. How far into January
depends on whether Nevada Republicans opt into or out of the February 6 presidential primary.
Again, I am interested in better informing readers. This is not about trying to drag The Green Papers and drive traffic from there to here. There is room for both, and I stand by 99 percent of what Richard and Tony do over there. But we approach the calendar's evolution differently. And those differences matter. They matter when wrong information starts to filter into the broader conversations about the 2024 presidential nomination process. And February 5 (Iowa) and February 13 (New Hampshire) -- not to mention February 24 (Nevada and/or South Carolina) -- are wrong. Those are not the dates of those contests and will not be barring an unprecedented cave on the part of the president and the DNC on the Democratic calendar. The odds of that are long, perhaps not as long as Marianne Williamson or Robert Kennedy Jr. becoming the Democratic presidential nominee in 2024, but really, really long.
Iowa and New Hampshire may not end up where FHQ has them placed now either. The information environment could change again! But it is a near certainty that those contests will not be in early February given what we know now. If push comes to shove and one does not know how to describe it, then just say that Iowa and New Hampshire will be early next year. No, that may not be as specific as some want, but it is accurate at this time.
--
See more on our political/electoral consulting venture at FHQ Strategies.